Thyroid is butterfly shaped gland lies in front of the neck below the adam’s apple. It has 2 lobes connected to each other by isthmus.It weighs 25grams in adult,with each lobe being about 5 cm long, 3 cm wide, and 2 cm thick, and the isthmus about 1.25 cm in height and width.The gland is usually larger in women than in men, and increases in size during pregnancy.

Hormones secreted by thyroid gland-
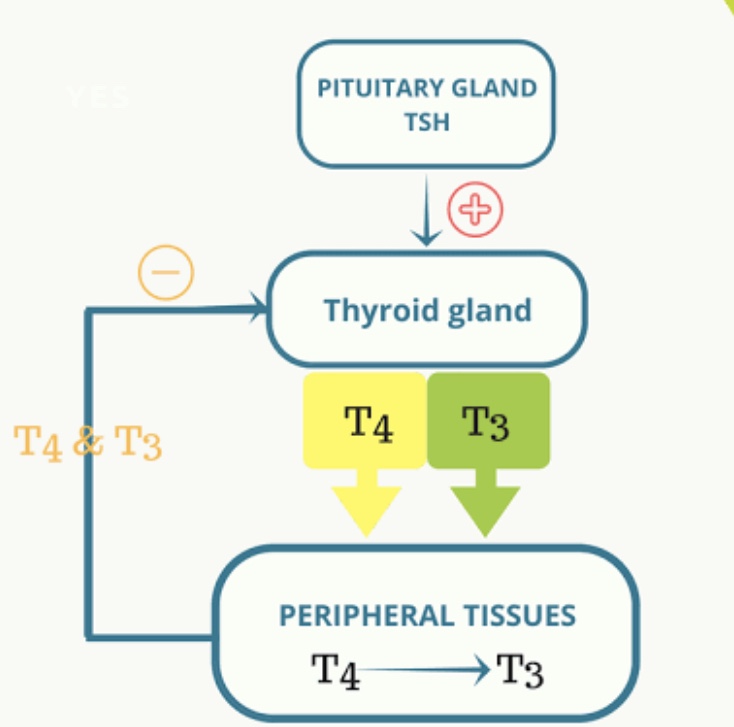
The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones – triiodothyroxine(T3) and thyroxine (T4)– and a peptide hormone, Calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium hemostasis. Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH), which is produced by the Hypothalamus.
Thyroid disorders-

Thyroid disorders includes
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Thyroid inflammation(thyroiditis)
- Thyroid enlargement(goitre)
- Thyroid nodules
- Thyroid cancer.
Hyperthyroidism
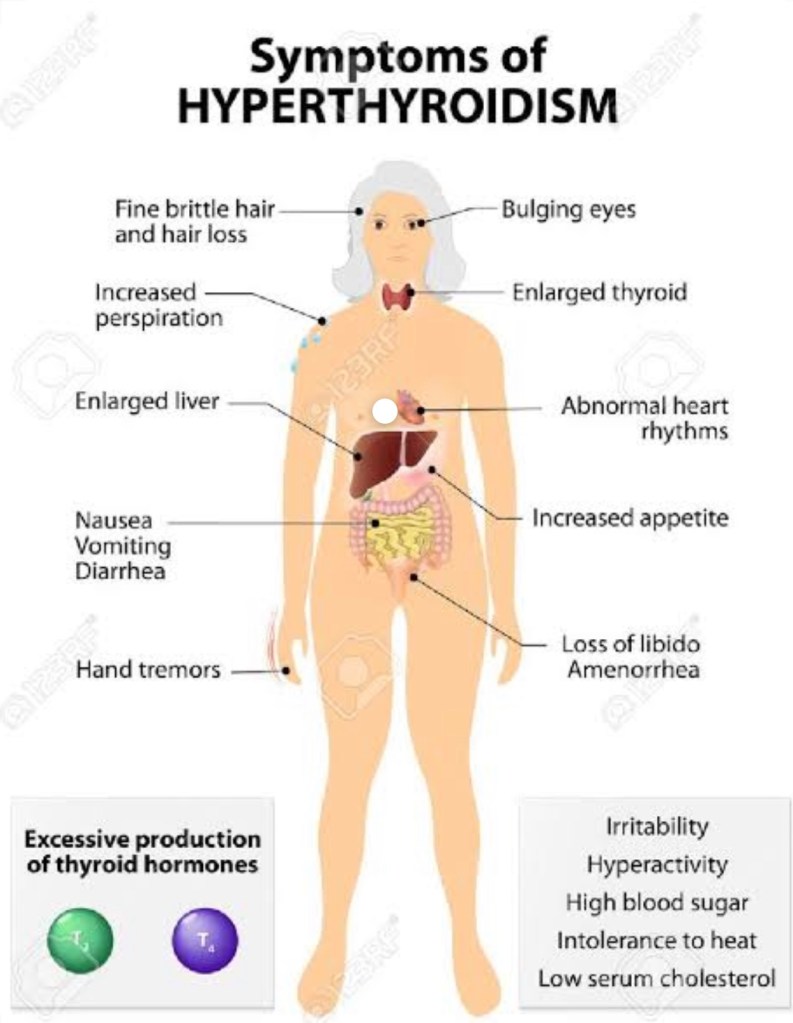
Hyperthyroidism– excessive secretion of thyroid hormone,the most common cause is the autoimmune disorder grave disease. Hyperthyroidism often causes a variety of non specific symptoms including •weight loss, increased appetite, •insomnia, •decreased tolerance of heat, •tremor, •palpitations, •anxiety and nervousness. In some cases it can cause •chest pain •diarrhoea,•hair loss and •muscle weakness. Such symptoms may be managed temporarily with drugs such as Beta blockers, propylthiouracil, Carbimazole, radioactive iodine-131
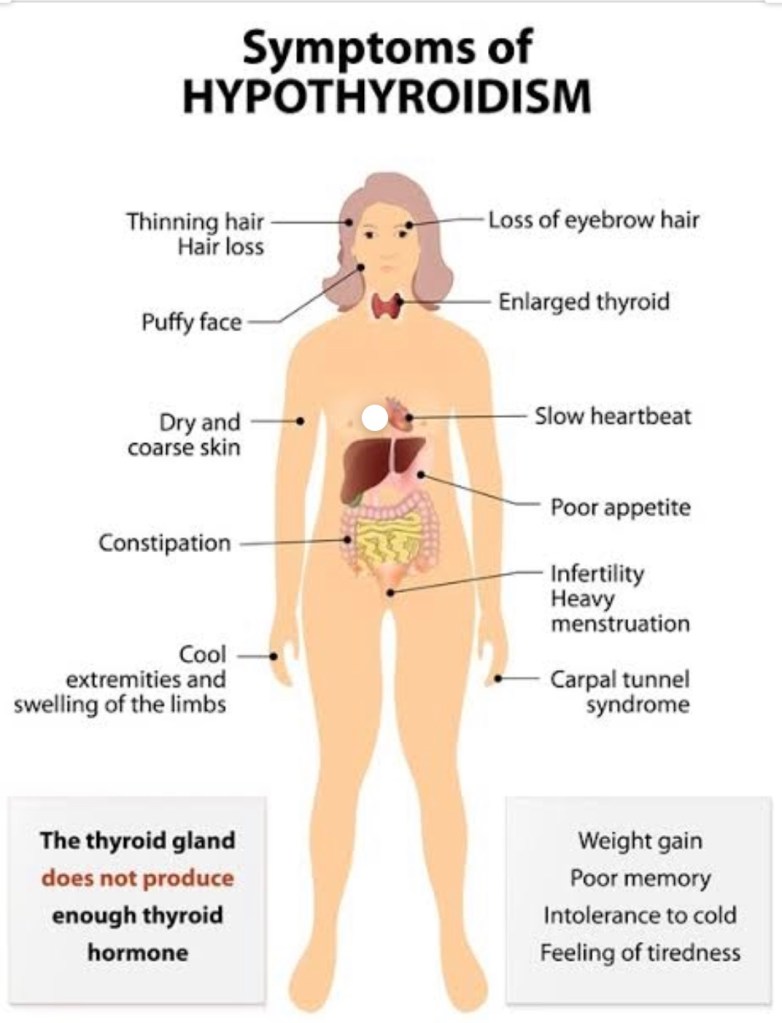
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism-deficient secretion of thyroid hormones,the most common cause is iodine deficiency. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is the autoimmune disorder Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
An underactive thyroid gland results in hypothyroidism. Typical symptoms are •abnormal weight gain, •tiredness, •constipation, •heavy menstrual bleeding,•hair loss, •cold intolerance, •slow heart rate. Some forms of hypothyroidism can result in Myxedema and severe cases can result in Myxedema coma.
Hypothyroidism is managed with replacement of the hormone Thyroxine. This is usually given daily as an oral supplement, and may take a few weeks to become effective.Some causes of hypothyroidism, such as Postpartum thyroiditis and Subacute thyroiditis may be transient and pass over time, and other causes such as iodine deficiency may be able to be rectified with dietary supplementation.
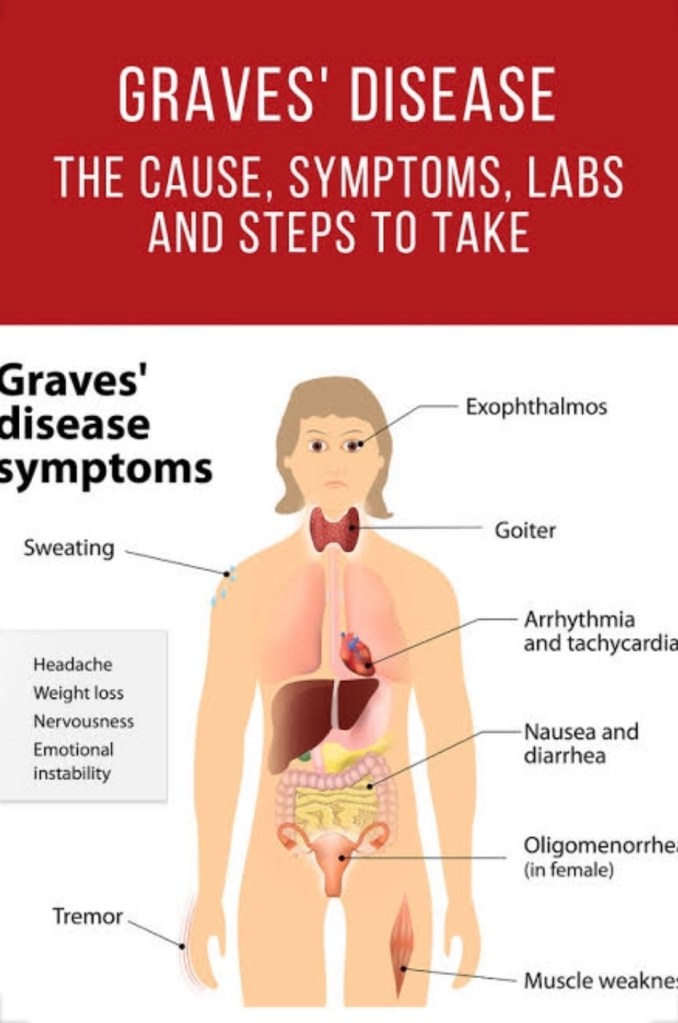
Grave’s disease
It is an autoimmune disorder that is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. In Graves’ disease, for an unknown reason antibodies develop against the thyroid stimulating hormone receptor. These antibodies activate the receptor, leading to development of a goitre and symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as heat intolerance, weight loss, diarrhoea and palpitations. Occasionally such antibodies block but do not activate the receptor, leading to symptoms associated with hypothyroidism.
Nodule
Thyroid nodules are often found in the gland with a prevalence rate of 4-7%.
When a nodule is present, thyroid function test determine whether the nodule is secreting excess thyroid hormones, causing hyperthyroidism. When the thyroid function tests are normal, an ultrasound is often used to investigate the nodule, and provide information such as whether the nodule is fluid-filled or a solid mass, and whether the appearance is suggestive of a benign or malignant cancer. A needle aspiration biopsy may then be performed, and the sample undergoes cytology in which the appearance of cells is viewed to determine whether they resemble normal or cancerous cells.
The presence of multiple nodules is called a Multinodular goitre and if it is associated with hyperthyroidism, it is called a toxic multinodular goitre.

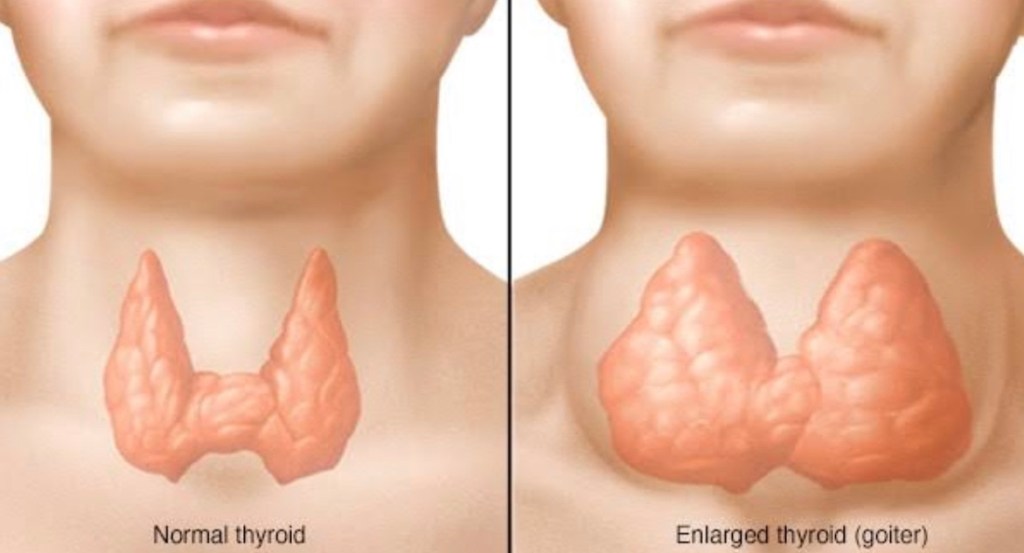
Goitre
An enlarged thyroid gland is called a Goitre. Goitres are present in some form in about 5% of people, and are the result of a large number of causes, including -iodine deficiency, -autoimmune disease (both Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis), -infection, -inflammation, and -infiltrative disease such as Sarcoidosis and amyloidosis. Sometimes no cause can be found, a state called “simple goitre“. Goitres may be associated with hyperthyoidism or hypothyroidism, relating to the underlying cause of the goitre.
Inflammation
Inflammation of the thyroid is called Thyroiditis, and may cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. Two types of thyroiditis initially present with hyperthyroidism and are sometimes followed by a period of hypothyroidism – Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and postpartum thyroiditis. There are other disorders that cause inflammation of the thyroid, and these include subacute thyroidits, acute thyroidits, silent thyroiditis,riedel’s thyroiditis,and traumatic injury, including palpation thyroiditis.
Cancer
The most common neoplasm affecting the thyroid gland is a benign adenoma, usually presenting as a painless mass in the neck. Malignant thyroid cancers are most often carcinoma, although cancer can occur in any tissue that the thyroid consists of, including cancer of C-cells and lymphomas.
Congenital
A persistant thyroglossal duct is the most common clinically significant congenital cause of the thyroid gland.
Iodine
Iodine deficiency most common in inland and mountainous areas, can predispose to goitre – if widespread, known as Endemic goitre. Pregnant women deficient of iodine can give birth to infants with thyroid hormone deficiency. The use of iodised salt to add iodine to the diet has eliminated endemic cretinism in most developed countries, and over 120 countries have made the iodination of salt mandatory.
Test-

Stay home। Stay safe।
Westayin।coronastayout।